聚会互认问题小记
前两天,由4位轮值主席组织的第一届游在长安活动正式落幕。在活动组织过程中,有一个小游戏的分组问题很有一次,在此记录。

This is an automatically translated post by LLM. The original post is in Chinese. If you find any translation errors, please leave a comment to help me improve the translation. Thanks!
A few days ago, the first "Game in Chang'an" event organized by four rotating chairpersons officially came to an end. There was a grouping problem in a small game during the event, and I will record it here.

年纪越大,感到时光流逝的就越快。转眼间,就已经到了2023年。比我大一届的师兄师姐们就要毕业了。这篇博客主要放照片用,没有什么太多的文字内容。
祝各位毕业的师兄师姐前程似锦,生活精彩。🎉🎉🎉

This is an automatically translated post by LLM. The original post is in Chinese. If you find any translation errors, please leave a comment to help me improve the translation. Thanks!
As we grow older, we feel that time passes by faster. In the blink of an eye, it's already 2023. The seniors who are one year older than me are about to graduate. This blog mainly consists of photos and doesn't have much text content.
I wish all the graduating seniors a bright future and a wonderful life. 🎉🎉🎉

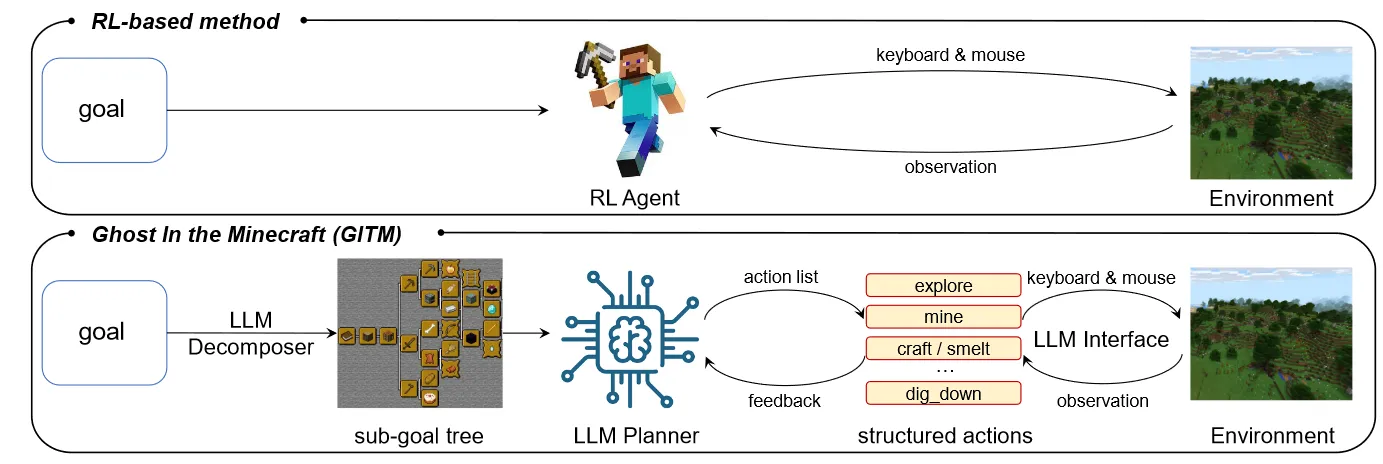
最近,清华大学和商汤发表了一篇名为《Ghost in the Minecraft: Generally Capable Agents for Open-World Environments via Large Language Models with Text-based Knowledge and Memory》的文章,简称GITM。很有意思,感兴趣的朋友可以读一下原文。
This is an automatically translated post by LLM. The original post is in Chinese. If you find any translation errors, please leave a comment to help me improve the translation. Thanks!
Recently, Tsinghua University and SenseTime published an article titled "Ghost in the Minecraft: Generally Capable Agents for Open-World Environments via Large Language Models with Text-based Knowledge and Memory," abbreviated as GITM. It's quite interesting, and interested friends can read the original article.

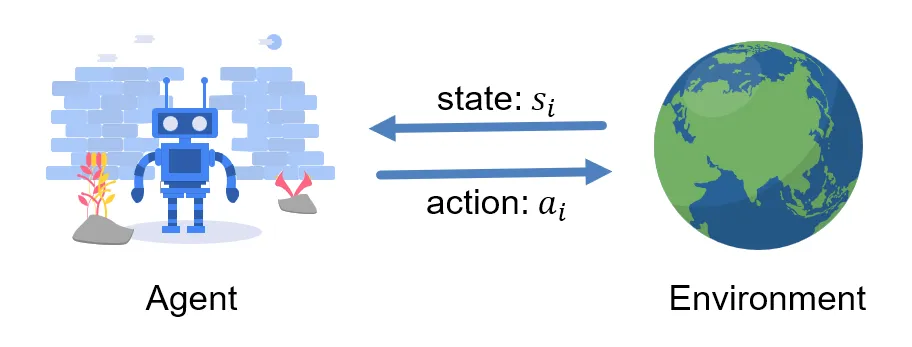
深度强化学习的流程可以抽象为以下步骤的重复:
本文主要探讨在收集经验过程中,环境自然结束(Terminated,包括目标成功,失败等)和人为截断(Truncated,主要为达到一定步数结束)对经验收集和训练产生的影响,以及如何对其进行处理。并对其进行了部分实验来比较性能。
This is an automatically translated post by LLM. The original post is in Chinese. If you find any translation errors, please leave a comment to help me improve the translation. Thanks!
The process of deep reinforcement learning can be abstracted into the following steps:
This article mainly discusses the impact of natural termination (Terminated), including successful or failed goals, and artificial truncation (Truncated), mainly ending after a certain number of steps, on experience collection and training. It also conducts some experiments to compare performance.

强化学习在算法实现时需要非常注意细节,否则网络很难收敛或没有训练效果。本文主要记录我在实现各种强化学习算法时踩到的一些坑以及需要注意的细节,持续更新......
以及附上我自己实现的RL算法库:https://github.com/KezhiAdore/RL-Algorithm

This is an automatically translated post by LLM. The original post is in Chinese. If you find any translation errors, please leave a comment to help me improve the translation. Thanks!
And here's my self-implemented RL algorithm library: https://github.com/KezhiAdore/RL-Algorithm
